geoprofil.co performs professional 3D laser scanning
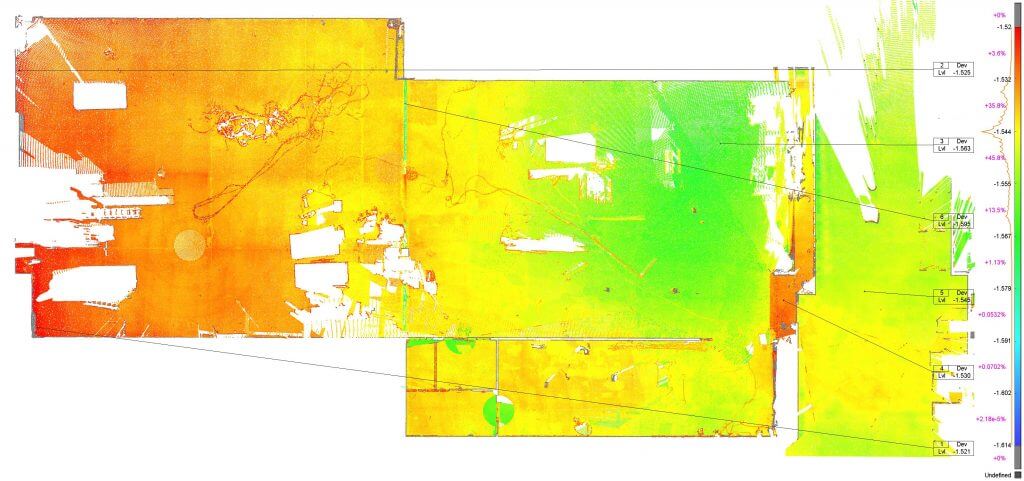
Laser scanning is a quick, effective and precise technique of obtaining three-dimension data of environment. Laser scanning enables geoprofil.co to take measurements of large objects in a much shorter time than the traditional method permit.
The measurements results can be used in several analysis and visualizations. 3D laser scanning offers a more detailed measurement of objects. Adequately it turns into quality and attractiveness of end result.
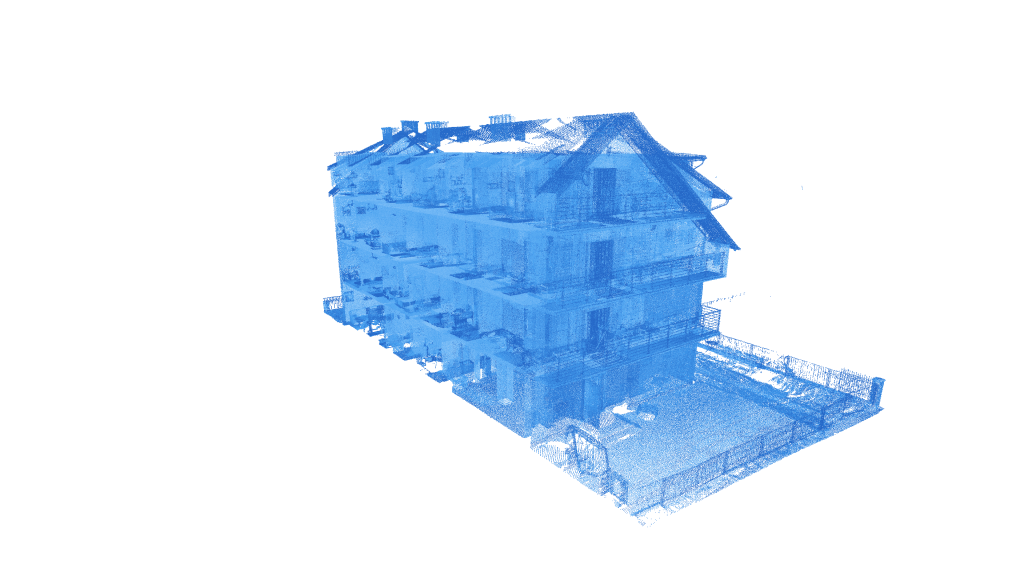
3D laser scanning – how it is carried out?
With use of laser and the prism rotating with very high speed in a short time (up to 2 million per minute) 3D laser scanning enables to obtain millions of points in a short time. After the first stage of scanning, the position of points against the laser as well as intensity of reflection is known. A series of photographs is taken at the next stage to give the points their actual color.
Information obtained through laser scanning, after pre-treatment – registration, cleaning, coloration, classification, constitute a huge set of points called point cloud. This cloud of points can then be imported to a wide spectrum of programs for analysis, vectorization or modelling.

6 situations in which you should go for laser scanning
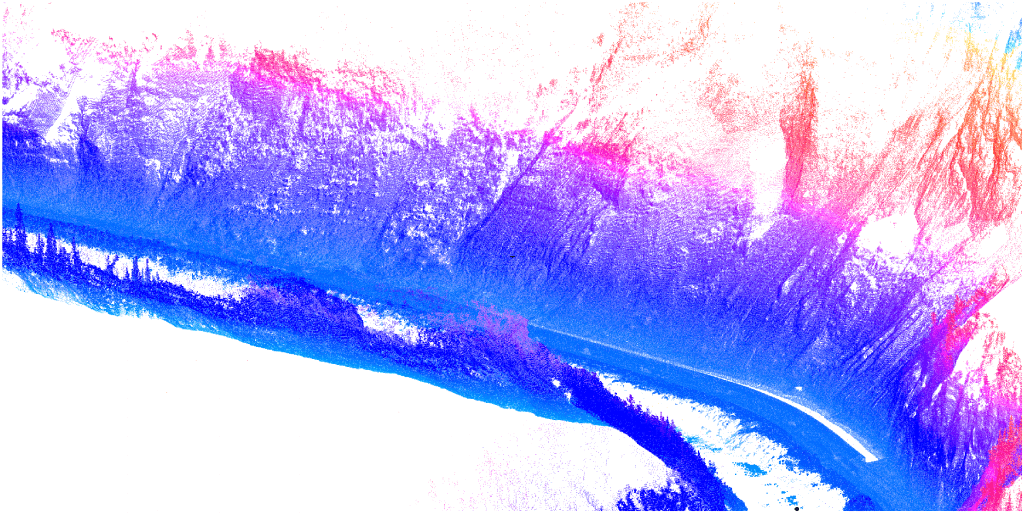
- Limited access to inventory object – unlike the traditional measurement methods, the visibility of measured elements alone is sufficient, one does need to touch or approach them.
- Limited time for measurements works– time used for measurement works is 2-5 times shorter than that of traditional methods. Peace of tenants and object users is disturbed shorter,
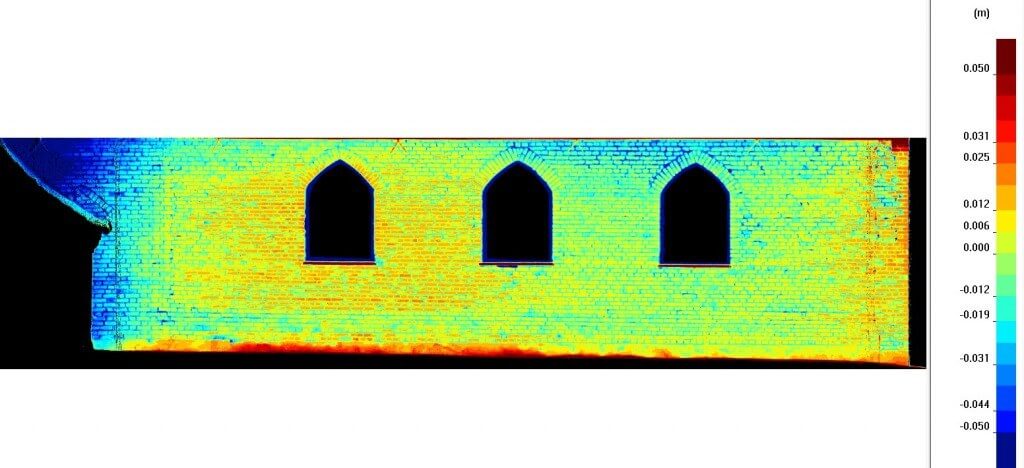
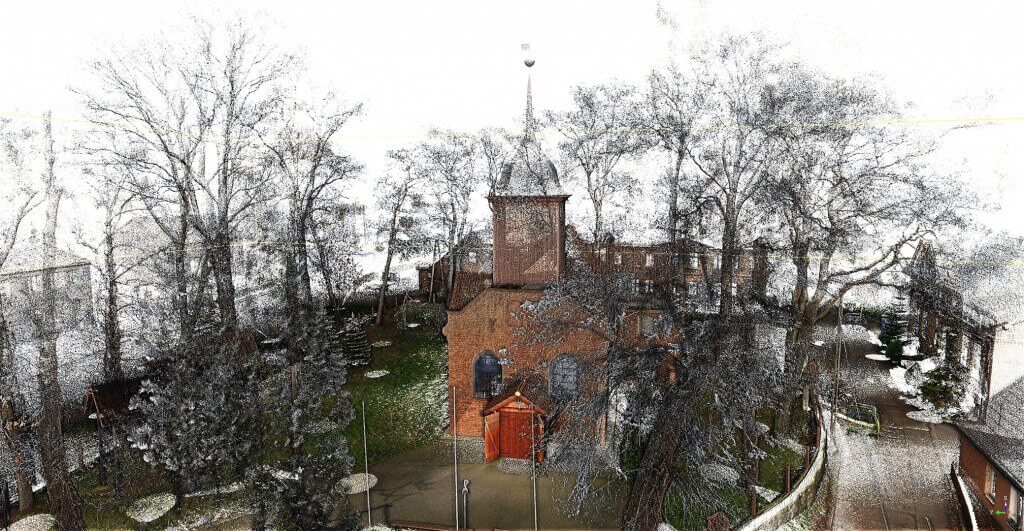
- Monumental objects, richly decorated – if you care for inventory of architecturally complex building or if you want to have its digital copy also called digital twin,
- You want to improve incorrect or incomplete object’s documentation – laser scanning is the perfect tool to verify the existing documentation,
- You need many studies (2D CAD, deformations, modelling) but you want to perform them in stages – during laser scanning one can gather all necessary data to prepare the whole range of elaborations. Remaining elaborations can be performed in stages based on single laser scanning,
- You need precise knowledge on object’s distortion – laser scanning unlike the traditional measurement methods (tachymetry, leveling) allows to detect complex distortions, deflections, sprains of the whole object’s surface.
Nowe Ogrody by geoprofil on Sketchfab
When you should not decide on scanning?
Laser scanning is one of many measurement techniques. As every technique it has advantages and disadvantages, strengths and weaknesses. Laser scanning has definitely more strengths than weaknesses but the strengths will no be felt in each case. In other situations similar effect can be obtained with a more efficient method.
Getting to the point:
- If the inventory object is very extensive – with surfaces of several dozens or several hundred of hectares – photogrammetry or combination of those methods can be more efficient. Raiding with the drone over an extensive area data can be obtained several times faster.
- If your inventory funds are particularly limited – laser scanning is not competitive pricewise as compared to the inventory method with use of measure or range finder scoop, especially with small objects. If you are satisfied with e.g. façade schemes and the detailed views are not necessary to you it is better to think over simpler methods.
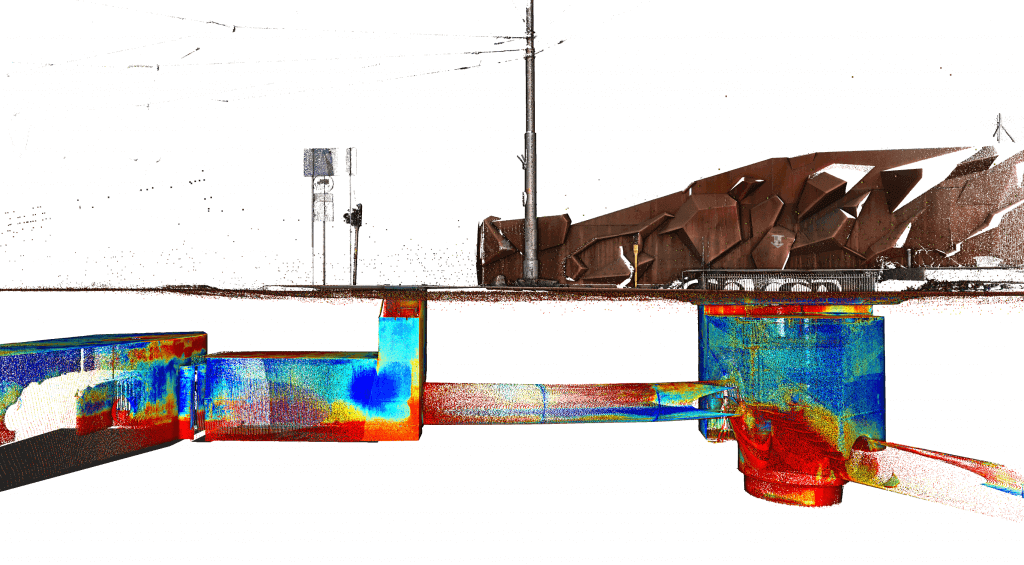
Laser scanning – application

The basic product of laser scanning – the point cloud can serve as the product itself, be freely dimensioned, be a reference to the project. It can also be the output product for further elaborations.
Laser scanning has a wide spectrum of applications:
Architecture:
- Buildings’ inventory – laser scanning of architecture for need of modification or expansion
- Monitoring of construction works advancement
- 2D CAD documentation preparation
- 3D CAD models preparation
- Generation of high resolution orthoimages
- Scanning to BIM
Monuments:
- Precise inventory for renovation
- Monitoring of object’s deformation
- 2D CAD documentation preparation
- 3D CAD models preparation
- Laser scanning of the terrain
Infrastructure:
- Creating of topographic maps in 2D and 3D
- Creating numeric model of the terrain
- 3D laser measurement of rail roads in order to control the gauge
- Analysis of construction works advancement
Industry:
- 3D measurements of halls and other large scale objects
- Elaboration of PDMS models
- Creation of 2D CAD drawings
- Spatial analysis – deformations, collisions
Engineering:
- Measurement of verticality and planarity – examination of deformation,
- Dimensional control of components of any shape
- Landfills for loose materials
- Heap volume measurements
- Cloud of points as the result of laser scanning

